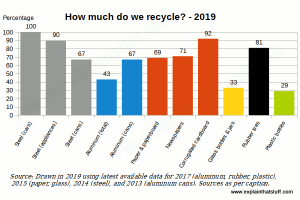
Recycling Basics
Recycling is the process of taking used materials and reconstituting them for reuse. For example, used aluminum, a commonly recycled material, is melted and re-shaped to form new cans, tins, etc. Recycling is useful because it allows manufacturers to use already-produced materials instead of having to mine and smelt more ore, melt more silica to glass, or cut down more trees for wood pulp. Unfortunately, some otherwise recyclable materials are not collected in every community, so materials that could be reused are thrown away instead. In addition to environmental benefits, recycling also has economic benefits. In the United States, the recycling industry employs 681,000 people, produces $37.8 billion in wages and contributes $5.5 billion in tax revenue as of 2016. This means that each 1,000 tons of recycled material creates 1.17 jobs, and each ton produces $65.23 in wages and $9.42 in taxes.